(I) Overview The essence of ion exchange adsorption is the metathesis reaction between the target component ion and the solid ion exchanger in the solution, so that the target component is selectively transferred from the liquid phase to the solid phase, and then the target group is made with the corresponding reagent. The fraction is re-introduced into the liquid phase to separate and concentrate the component of interest. The process of transferring the target component from the liquid phase to the solid phase is generally referred to as adsorption, and the process of transferring from the solid phase to the liquid phase is referred to as leaching.

The principle flow of the ion exchange method is shown in Figure 1. Adsorption and leaching are the two most basic operations of the process. Usually, after these two operations, there are washing operations. The backwash after adsorption is to wash away the original solution and the impurities with low affinity. The rinse after rinsing is washed and rinsed. Agent. The rinsed resin is sometimes sent for transformation, and the transformed resin is returned to the adsorption operation.
The most commonly used solid ion exchangers are various types of ion exchange resins and activated carbon.
Ion exchange adsorption is commonly used to extract useful components from dilute solutions, separation of rare earths, and purification of wastewater.
(II) Ion exchange resin The ion exchange resin is an organic polymer compound having a three-dimensional porous network structure and containing an exchange group and insoluble and infusible. The unit structure is composed of an insoluble three-dimensional network skeleton and an exchange group attached to the skeleton. The group (fixed ion) and the opposite charge ion (exchangeable ion) carried by the exchange group are composed of three parts. The exchange groups are evenly distributed in the network skeleton, and the mesh in the skeleton allows free exchange of ions.
The full name of a domestic ion exchange resin consists of a classification name, a skeleton (or group) name, and a basic name arrangement. The ion exchange resin is divided into a gel type and a macroporous type, and is a macroporous resin having a physical pore structure. The redox resin name consists of a group name, a skeleton name, a classification name, and a resin arrangement.
The model of the domestic resin consists of five digits, and the meaning of each value is shown in Figure 2. Domestic resin is divided into seven categories, and the skeleton is also divided into seven categories.

The old model of domestic resin consists of three digits, starting with "7", the second digit indicates the type, "0" is weak base, "1" is strong alkali, "1" is weak acid, and "3" is strong acid. The third digit is the sequence number.
(3) Activated carbon adsorption adsorption method is one of the effective methods for extracting, separating and enriching the target components from dilute solutions. The most commonly used adsorbent is activated carbon, which is a carbonized carbonaceous material at a high temperature (600-900 ° C), and then activated at 400-900 ° C with air, carbon dioxide, water vapor or a mixture thereof. Substance with a very large specific surface area. Currently, it is mainly used for extracting gold , silver and wastewater treatment.
The principle flow of activated carbon adsorption is basically the same as that of the ion exchange method, but sometimes the gold-loaded carbon can be burned and then gold is extracted. [next]
(4) Basic parameters
The basic parameters are listed below:
(1) Full capacity: is the maximum or ultimate exchange capacity, which is the number of exchange groups per unit of resin (weight or volume), regardless of the exchange ion type and operating conditions. The weight capacity expressed by the weight of the resin and the volume of the resin are referred to as the volumetric capacity. According to the habit of analyzing work, the unit can use millimolar [r] / liter or millimolar [r] / gram.
(2) Operating capacity (working capacity): refers to the exchange capacity of the resin during adsorption equilibrium under operating conditions, and its value is generally less than the full capacity.
(3) Leakage capacity: The actual capacity of the resin when the concentration of absorbed ions in the effluent reaches a certain value under certain operating conditions during column operation.
(4) Saturated capacity: The exchange capacity of the resin when the concentration of the absorbed ions in the effluent is the same as the concentration of the ions in the original solution under a certain operating condition during column operation.
The exchange capacity is limited to a typical ion exchange process (such as exchange between inorganic ions), but the resin also has an adsorption capacity, so the exchange capacity measurement value also includes a certain amount of adsorption amount.
(5) Selectivity coefficient: the ratio of the concentration of two ions in the liquid phase to the concentration ratio of the two phases in the liquid phase when a certain amount of resin is contacted with a solution containing a known concentration of A, B ions.
(6) Concentration ratio (distribution coefficient): The ratio of the total concentration of absorbed ions in the resin phase to the total concentration in the liquid phase during adsorption equilibrium.
(7) Separation factor: Under certain operating conditions, the ratio of the partition coefficients of the absorbed ions A and B is equal to the selectivity coefficient when exchanged between counterions of equal charges.
(8) Adsorption isotherm: The relationship between the concentration of the absorbed ions in the resin crucible and the concentration in the solution at a constant temperature under a certain operating condition.
(V) Ion exchange adsorption research and application technology Ion exchange adsorption test research generally includes the following:
(1) The resin type is selected in accordance with the existence form of the target component.
(2) Screening the resin with the desired solution.
(3) Study the effects of the composition of the aqueous phase: pH of the solution, concentration of the absorbed component, concentration of the impurity component, concentration of the oppositely charged ion, and the like.
(4) Study the effects of resin properties: skeleton, degree of crosslinking, pore structure, particle size, mechanical strength, and exchangeable ion type.
(5) Influence of operating parameters: flow rate, temperature, height-diameter ratio of resin bed, adsorption isotherm, and adsorption kinetic curve.
(6) Effects of eluent and rinsing parameters: eluent composition, single reagent or mixed reagent, concentration, rinsing flow rate and temperature.
(7) Treatment of qualified eluent.
(8) Adsorption-rinsing multiple cycles test: resin transformation, treatment of poisoning resin, etc.
(6) Ion exchange equipment
The classification of ion exchange equipment is summarized as follows:

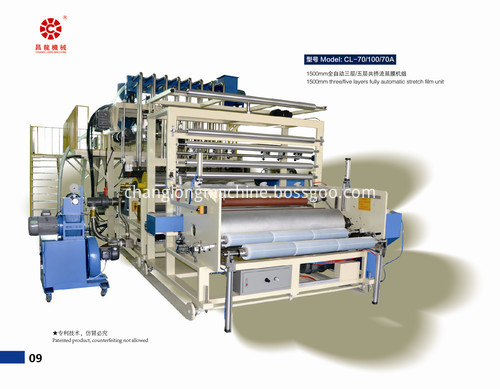
With more than 30 years customers` actual operation and technology improvement, 1500mm two/three/five layers fully automatic stretch film machine is mature and cost-effective, some whole production line adopt melt metering pump technology and high precision pressure sensor system, which can stably and effective to control the pressure. It will highly improves film horizontal and vertical`s tension strength and anti-puncture resistance and make the film meeting the high requirement for machine packing film. The cooling roller adopts big diameter design and special double-decker runner, greatly improving the cooling effect of high-speed production to guarantee good uniformity of cooling roll surface temperature. The film produced by this machine has good shrinking memory function and self-sticky, which can be widely used in wrapping of palletized goods. It`s good substitute for hot shrinking packing film during transportation.
*Related Products:pe casting film machine,pe cling film machine,pe protective film machinery.
Machine Pictures:

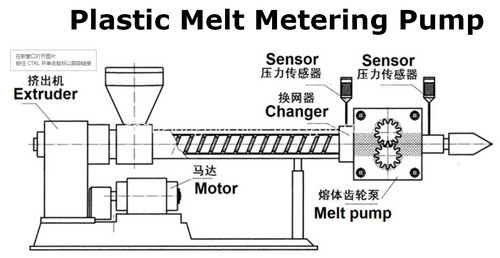
Plastic melt metering pump is more and more important in extrusion process, especially in high-end products industries, such as high quality sheets, pipes, BOPP, optical cable.
Installing the melt metering pump in the cast stretch film unit, which can keep the production constantly and efficiency. The pump can improve the product quality, stable the production and decrease the energy consume.
The housing is made of chromium-nickel alloy or nickel-base alloy, titanium alloy. The gear is made of quenching chromium steel, other metal materials are also applicable. Bearing is made of graphite NIAG, zirconium oxide or quench tool steel.
Advantages:
FAST AND STABLE FLOW SUPPLY
Eliminated the extruder`s pulsation wave. Improve the product quality, decrease the defective rate, and decrease the waste, which can save 2% material and 25% of the unit power consumption.
STABLE AND EFFICIENCY PRESSURE CONTROL
The melt pump can provide a stable pressure, which short the discharge time obviously and make the production effectively.
INCREASE THE EXTRUDER OUTPUT AND THE MACHINE LIFE
It has been found that after install the melt pump, the max pressure wave value is the pressure after pump. Which can make the inner pressure of the extruder decrease, the melt shear strength decrease, the temperature curve gently, and restrain the temperature rising. Also the melt pump can avoid the damage to the extruder from the high pressure.
Produced Films
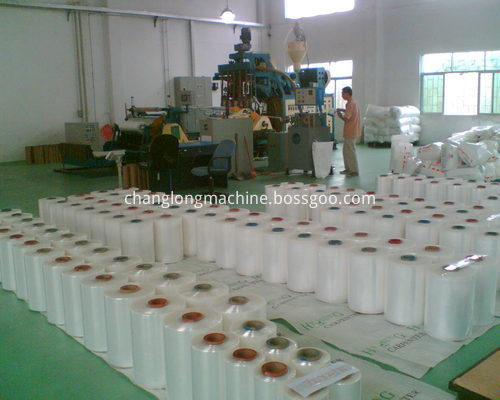



1500mm stretch film machine unit
1500MM Black Stretch Film Machine Unit,1500MM Hand Stretch Film Machine Unit,1500MM Plastic Stretch Film Machine Unit,1500MM Packaging Stretch Film Machine Unit
CHANGLONGXING SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY (SHENZHEN) CO.,LTD , https://www.clxmachinery.com